Last updated: February 2026
Detached HEAD state lets you check out any commit in GitKraken Desktop without creating a branch. This is useful for reviewing or experimenting with past changes without affecting your active branches.
Quick Start
Use GitKraken Desktop to enter, work in, and safely exit detached HEAD state.
To enter detached HEAD state:
- Right-click any commit in the Commit Graph.
- Select Checkout this commit. The commit will display a
HEADlabel.
To preserve commits made in detached HEAD state:
- Right-click the commit labeled
HEAD. - Select Create branch here and name the new branch.
To exit detached HEAD state:
- Double-click any local branch in the graph or Left Panel to check it out.
Any commits made in detached HEAD state that were not saved to a branch will be removed when you switch branches. If you switch branches before creating a branch, use the Undo button if available, or run git reflog in the terminal to find the lost commit SHA and re-check it out with git checkout <SHA>.
Enter Detached HEAD State
- Right-click the commit you want to inspect.
- Select Checkout this commit.
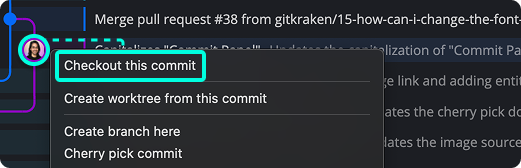
The checked-out commit will display a HEAD label, indicating you’re in detached HEAD state.
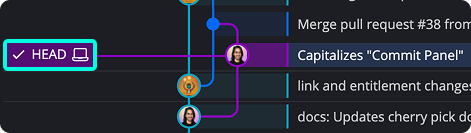
You can now review the full history and diffs, or create a branch from this state.
Commit in Detached HEAD State
You can make changes and commit them while in this state. However, these commits won’t belong to any branch.
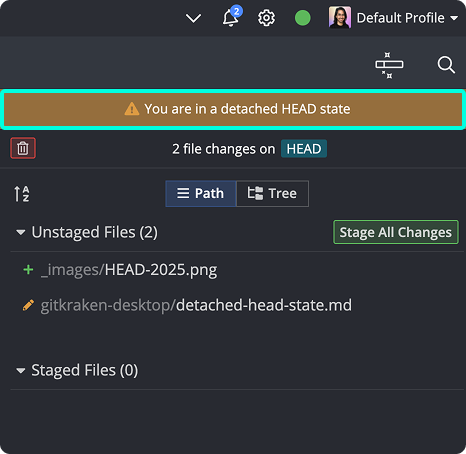
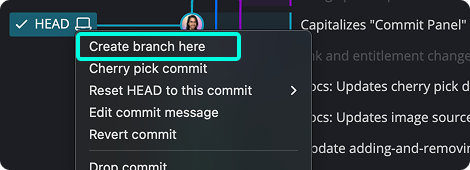
To preserve your work, create a branch from the current commit:
- Right-click the commit tagged as HEAD.
- Select Create branch here.
Exit Detached HEAD State
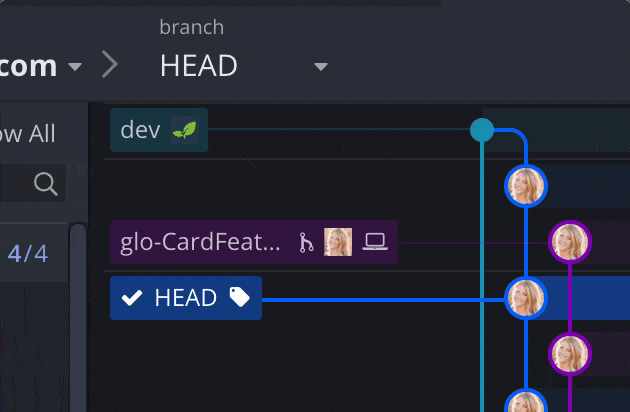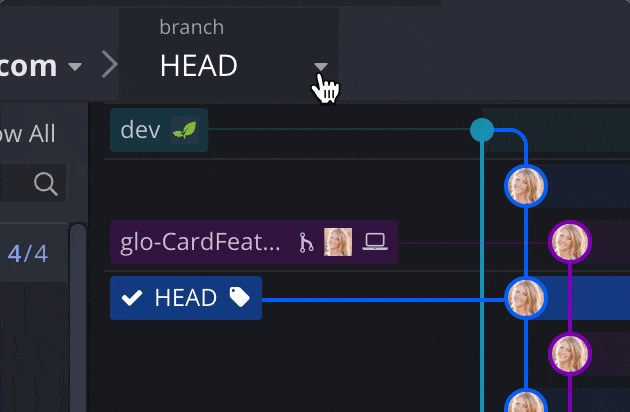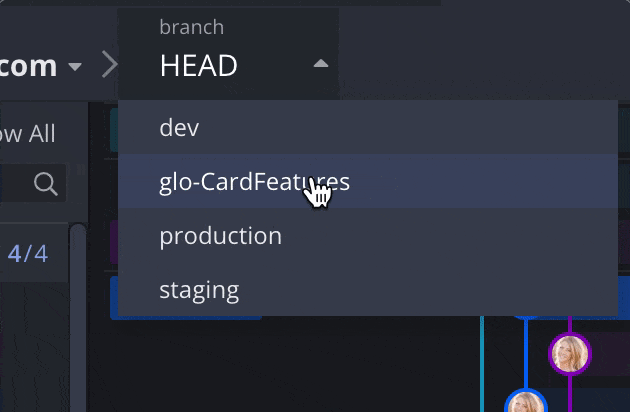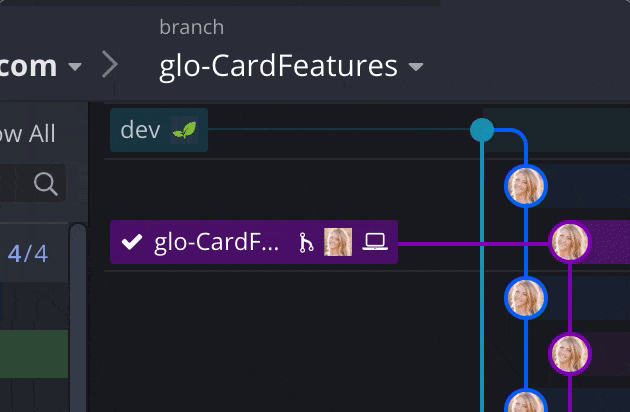
To exit detached HEAD state:
- Check out any local branch.
This will remove the HEAD label and discard any unpreserved commits.
Important: Commits made in detached HEAD state will be lost unless you create a branch. You may be able to recover them manually.
Recover Lost Commits
If you accidentally switch branches before saving your changes:
- Click Undo in GitKraken if available.
- Use the CLI and run
git reflogto find the lost commit SHA. - Then use
git checkout <SHA>to re-enter that state.