Integrate Tracked Folders with Jira Data Center
Quickly learn how to connect Tracked Folders via Git Integration for Jira Data Center app.
What’s on this page:
- Integrate Tracked Folders with Jira Data Center
- Limitations
- Introduction
- Connecting to a tracked folder
- Folder depth setting
- JMESPath filter setting
- Editing a tracked folder
- Removing a tracked folder
- Resetting index
- Viewing tracked repositories
- Reindexing a tracked folder
- Viewing git commits in Jira Data Center
- Jira administrators
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- More Integration Guides
Limitations
Pros:
- Less storage is required (the repositories are not cloned to Jira).
Cons:
- Only commits and branches get indexed with this method.
- Pull/merge requests are not indexed with this method.
- The create branch/pull request feature does not work.
Introduction
This feature scans a locally accessible path for cloned Git repositories and automatically imports those Git repository references into Jira. A repository group called FOLDER is added into the Git Integration for Jira app repository settings.
Connecting to a tracked folder
To add repositories via Tracked Folders:
-
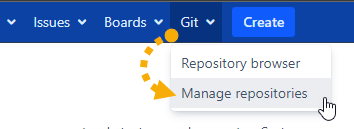
Go to Manage Git Repositories (Jira Dashboard ➜ Git menu) in Jira Data Center.
-
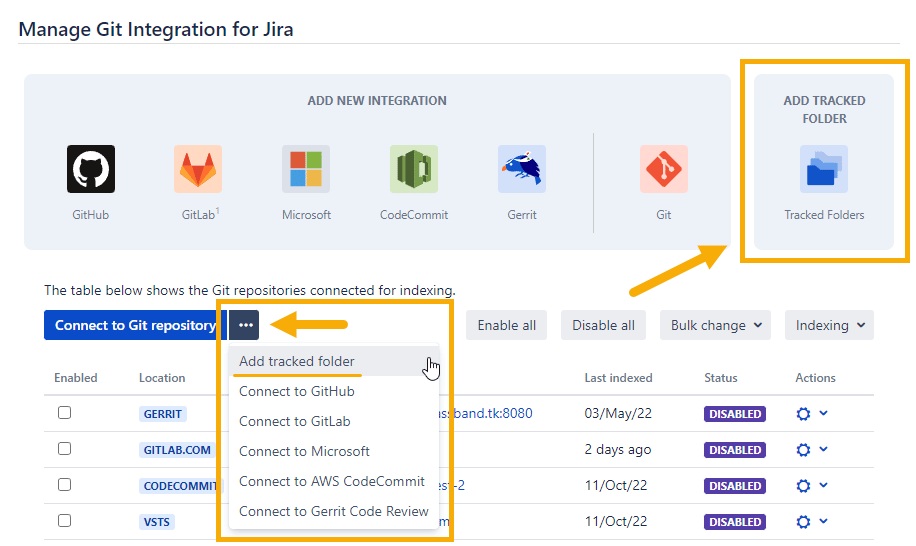
Click the dropdown arrow on Connect to Git Repository then Add tracked folder. The following dialog is displayed.
-
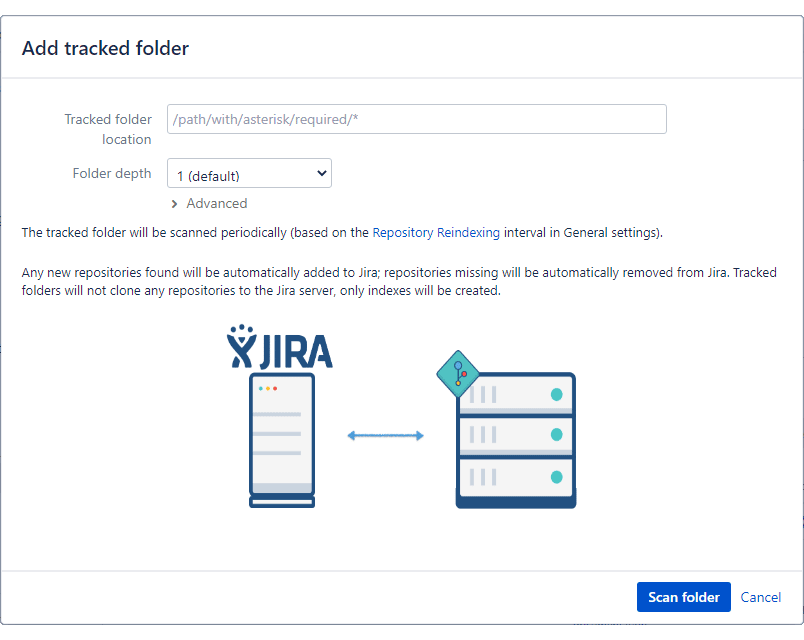
Enter the Tracked folder location in the required field. For this feature, a local path to the git repository residing on the same server as Jira is required. For example:
/home/ec2-user/repositories/*. -
Set the Folder Depth according to your organization’s requirements. For more information on this feature, see the Folder Depth section below.
-
OPTIONAL Expand the Advanced twisty to set the JMESPath options (see more details below) to filter connected repositories to Jira.
-
-
In the following dialog, the wizard will find git repositories stored in the provided path and displays the list of repositories found.
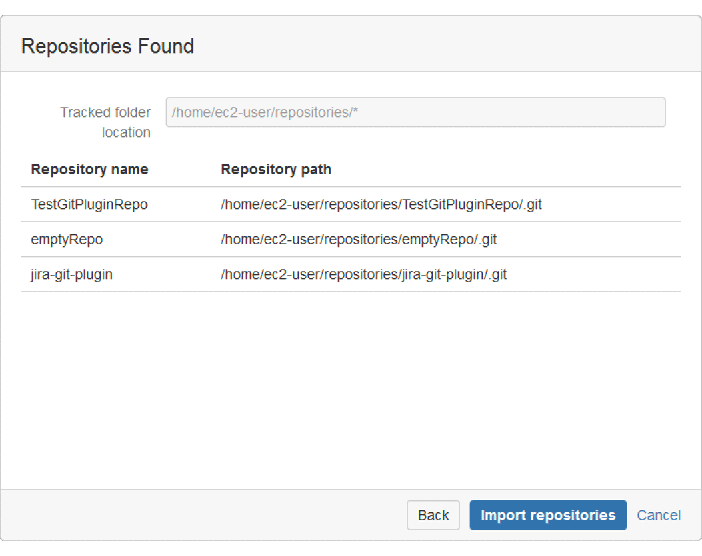
In the above example repository root,
/home/ec2-user/repositories/*, all repositories under this mask (/home/ec2-user/repositores/TestGitPluginRepo,/home/ec2-user/repositores/emptyRepo, … ,/home/ec2-user/repositores/jira-git-plugin) will be handled as one entry in the Manage Git repositories configuration page. For other features, these are treated as separate repositories. -
The Add tracked folder wizard scans the local path one folder level deep or depending on the Folder Depth setting. Click Import repositories.
The wizard automatically adds the detected repositories to Jira. If a repository is added to the path, Jira will add it to the index. If a repository is removed from the path, Jira will drop the index for that repository. -
On the Settings dialog, set Repository Browser, Smart Commits and Project Association permissions, if required. Click Next.
-
Click Finish to complete adding the tracked folder.
The tracked folder is added to the repository configuration list.
You can add multiple tracked folders in case your repositories are spread among multiple locations.
Folder depth setting
GitLab 13+ switched to hashed storage as the default. Git Integration for Jira app also supports this move by implementing support to tracked repositories with a new folder depth option for the GitLab hashed storage.
In GitLab 13.0, hashed storage is enabled by default and the legacy storage is deprecated. Support for legacy storage will be removed in GitLab 14.0.
The default tracked folder depth value is 1. For GitLab hashed storage support, our recommended setting is 3.
See GitLab docs on Hashed Storage for detailed information.
JMESPath filter setting
This optional setting is a filter on how repositories are listed and displayed.
The following examples of JMESPath filters work for any tracked folder integration including GitLab hashed storage folders (Connect to Git Repository ➜ Add tracked folder):
Lists repositories with names containing “git”
[?contains(name, 'git')]Lists all the repositories that contain the specified names
[?contains(name, 'git') | contains(name, 'Slap') | contains(name, 'est')]Excludes repositories with names that contain words ‘firstword’ and ‘secondword’
[?!contains(name, 'firstword') | contains(name, 'secondword')]The example below ONLY works for tracked folder integration; where it supports the ‘fullPath’ field:
Excludes repositories from the sub-folder
[?!starts_with(fullPath, '/home/user/local/store/private-repos')]
Editing a tracked folder
On the Manage Git repositories settings page, click ![]() Actions ➜ Edit tracked folder to modify tracked folder git repository settings.
Actions ➜ Edit tracked folder to modify tracked folder git repository settings.

Removing a tracked folder
On the Git Repositories settings page, click ![]() Actions ➜ Delete tracked folder to remove the tracked folder configuration from Jira.
Actions ➜ Delete tracked folder to remove the tracked folder configuration from Jira.
A confirmation prompt will be displayed. Clicking Remove will only remove the tracked folder setting from the repository configuration list. The local path for this tracked folder will not be deleted and will still remain in the local system for later use.
Resetting index
On the Git Repositories settings page, click ![]() Actions ➜ Reset index.
Actions ➜ Reset index.
This action will reset the indexes of the repositories for the selected tracked folder.
Viewing tracked repositories
On the Git Repositories settings page, click ![]() Actions ➜ Show tracked repositories.
Actions ➜ Show tracked repositories.
This action will open the Tracked Folder dialog showing the tracked repositories.
The Repository Browser will not display the repository if it is disabled in the Git Repositories configuration. The commits and code diffs in the Issue ➜ Git Commits, Git Roll Up and Project tabs will also be unavailable due to this.
Reindexing a tracked folder
On the Manage Git repositories settings page, click ![]() Actions ➜ Reindex tracked folder.
Actions ➜ Reindex tracked folder.
This action will perform a reindex of the selected tracked folder.
If a new repository is manually added into the local path, the Git Integration for Jira app will detect the new repository folder on the next reindex and add it into the existing tracked folder in Jira.
If a repository folder is manually deleted from the local path, the Git Integration for Jira app will remove the repository setting from the tracked folder in Jira on the next reindex.
Viewing git commits in Jira Data Center
-
Perform a git commit by adding the Jira issue key in the commit message. This will associate the commit to the mentioned Jira issue.
-
Open the Jira issue.
-
Scroll down to the Activity panel then click the Git Commits tab.
-
Click View Full Commit to view the code diff.
Jira administrators
It is possible to track all repositories hosted on a GitLab server from inside a Jira server:
-
Setup NFS server on the GitLab computer
-
Mount GitLab repositories folder as a remote NFS folder on Jira server
-
Configure NFS permissions to allow Jira to access GitLab folders by using either of the two possible solutions:
Solution 1
The 'all_squash' option must not be used in the NFS server ‘etc/exports’ file for GitLab folders. The NFS client should have the ‘git’ group with the same GID as the ‘git’ group on the NFS server. The Jira user on the NFS client should be added to the group ‘git’.
Example of ‘/etc/exports’ line:
/var/opt/gitlab/git-data/repositories/testrepo xx.xx.xx.xx/24(ro,root_squash,async)Solution 2
Use the 'all_squash,async,anonuid=$uid,anongid=$gid' option on the NFS server, where $uid and $gid are the user ID and group ID for ‘git’ user and ‘git’ group respectively (or another user/group which you are using to access GitLab repositories on GitLab server).
/var/opt/gitlab/git-data/repositories/testrepo xx.xx.xx.xx/24(ro,all_squash,async,anonuid=497,anongid=497)In both cases either 'ro' or 'rw' options may be used on the NFS server.
More Integration Guides
GitHub.com (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
GitHub Enterprise Server (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
GitHub App integration (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
GitLab.com (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
GitLab CE/EE (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
Azure DevOps | Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS) (Git Integration for Data Center/Jira Server)
Azure DevOps Server | Team Foundation Services (TFS) (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
AWS CodeCommit (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
Gerrit (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
Bitbucket Server (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
Bonobo (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
Windows Network | Server Share (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)
Tracked Folders (this page)
Back to: Integration basics (Git Integration for Jira Data Center/Server)